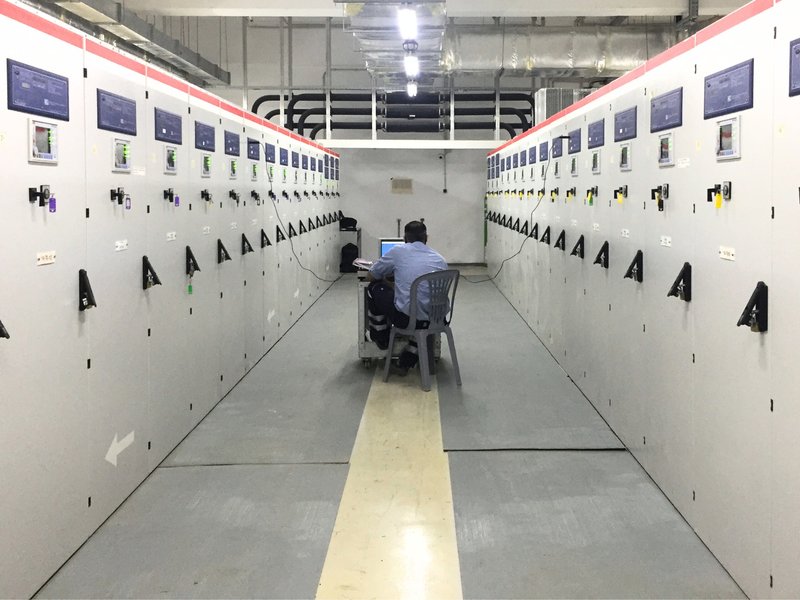
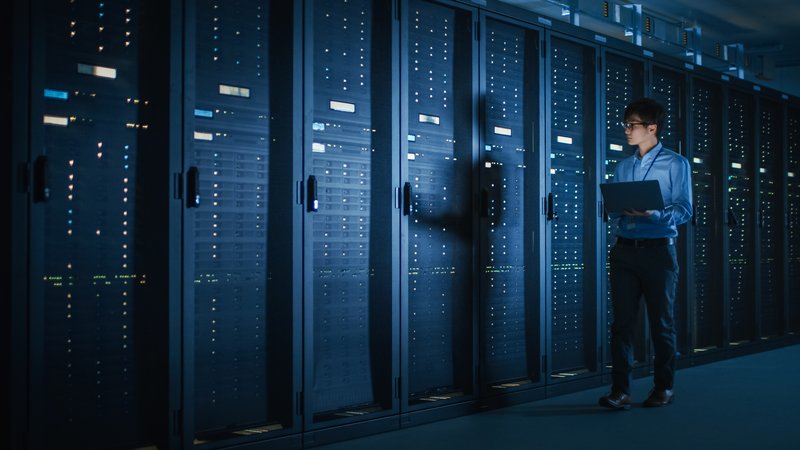
Equipment sizing verification ensures that installed electrical equipment, including transformers, power cables, switchgears, etc., is adequate to serve the electrical loads. Oversized equipment may lead to inefficient operation and increased costs, while undersized equipment can result in equipment failures and operational disruptions.
By verifying equipment sizing, engineers can mitigate risks, optimize performance, and achieve long-term cost savings, thereby supporting the overall reliability and sustainability of power infrastructure.
Key components
- Load flow analysis: ensure that voltage level and loading of electrical equipment remain within acceptable limits during normal and emergency operating conditions.
- Short circuit analysis: verify that electrical equipment can withstand short-circuit currents for a specific short-time period (until protective devices clear the fault), as well as interrupt the expected fault currents.
- Insulation coordination: verify that the insulation level of electrical equipment, including surge arresters, has been properly selected.
- Current transformer (CT) & voltage transformer (VT) adequacy study: ensure the adequacy of selected CT and VT ratings, in terms of accuracy and saturation, considering the requirements of the actual devices connected to them.
- Cable ampacity calculation: verify that cables can safely carry the expected electrical currents without exceeding thermal limits, considering the actual installation method.