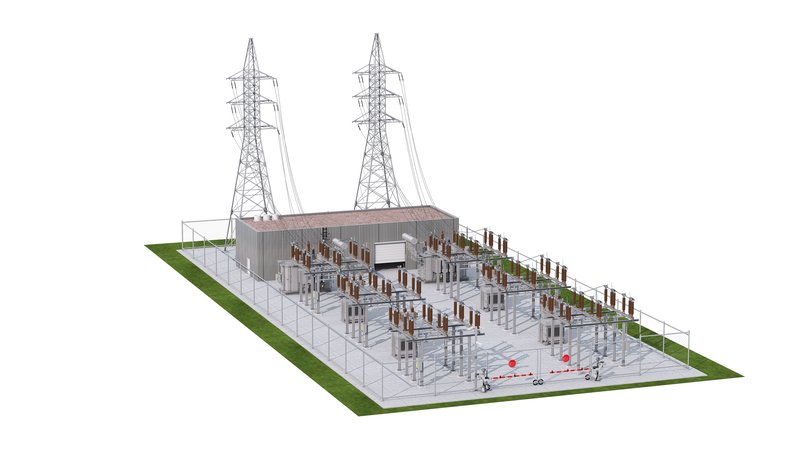
Key considerations include:
- Arrange components to ensure safe operation and facilitate easy monitoring, control, and maintenance.
- Design for redundancy in critical components to maintain operation during failures or maintenance.
- Facilitating the flow of power from incoming transmission lines to outgoing distribution feeders.
- Providing flexibility for future expansion and modifications.
- Ensuring compliance with local, national, and international standards and regulations regarding substation design and operation.
Common substation layouts include:
- The incoming overhead lines or cables area
- The high voltage Air Insulated Switchgear (AIS) or Gas Insulated Switchgear (GIS) equipment
- The medium voltage equipment
- The control building and the auxiliary systems areas.